The software behind GOOGLE search technology conducts a series of simultaneous calculations requiring only a fraction of a second. Traditional search engines rely heavily on how often a word appears on a web page. GOOGLE use more than 200 signals, including GOOGLE patented PageRank™ algorithm, to examine the entire link structure of the web and determine which pages are most important. Then GOOGLE conduct hypertext-matching analysis to determine which pages are relevant to the specific search being conducted. By combining overall importance and query-specific relevance, we're able to put the most relevant and reliable results first.
-
PageRank Technology: PageRank reflects GOOGLE view of the importance of web pages by considering more than 500 million variables and 2 billion terms. Pages that we believe are important pages receive a higher PageRank and are more likely to appear at the top of the search results.
PageRank also considers the importance of each page that casts a vote, as votes from some pages are considered to have greater value, thus giving the linked page greater value. We have always taken a pragmatic approach to help improve search quality and create useful products, and our technology uses the collective intelligence of the web to determine a page's importance.
-
Hypertext-Matching Analysis: GOOGLE search engine also analyzes page content. However, instead of simply scanning for page-based text (which can be manipulated by site publishers through meta-tags), our technology analyzes the full content of a page and factors in fonts, subdivisions and the precise location of each word. We also analyze the content of neighboring web pages to ensure the results returned are the most relevant to a user's query.
The life span of a Google query normally lasts less than half a second, yet involves a number of different steps that must be completed before results can be delivered to a person seeking information.
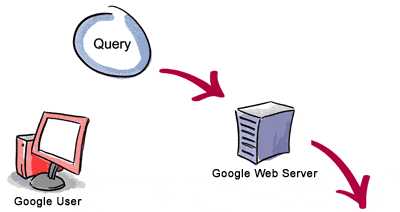
3. The search results are returned to the user in a fraction of a second.1. The web server sends the query to the index servers. The content inside the index servers is similar to the index in the back of a book - it tells which pages contain the words that match the query. 
2.The query travels to the doc servers, which actually retrieve the stored documents. Snippets are generated to describe each search result.

No comments:
Post a Comment